
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is responsible for secreting seminal fluid that transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when normal prostate cells reproduce uncontrollably. It usually develops slowly and doesn’t spread beyond the prostate gland. However, certain types of prostate cancer can spread aggressively in a short span of time.
In some cases, prostate cancer can metastasize when cancer cells break away from the prostate tumor and spread to other parts of the body through blood vessels or lymph nodes. After spreading, cancer cells can grow on tissues in other parts of the body and form new tumors. This is why screening for prostate cancer is so essential.
Prostate Cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death in men. Seniors who are 65 or older are more likely to be diagnosed with the condition than men under the age of 40. The specific cause of prostate cancer is unknown, however, there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing the condition. Age is the most prevalent risk factor. About 6 out of 10 men that are diagnosed with prostate cancer are 65 or older. Some men may also be at higher risk of developing prostate cancer due to genetic factors. The odds of being diagnosed with prostate cancer increase significantly if a first-degree relative, such as a father or brother, has already been diagnosed with the condition. Men of African American descent are also at an increased risk of developing prostate cancer.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
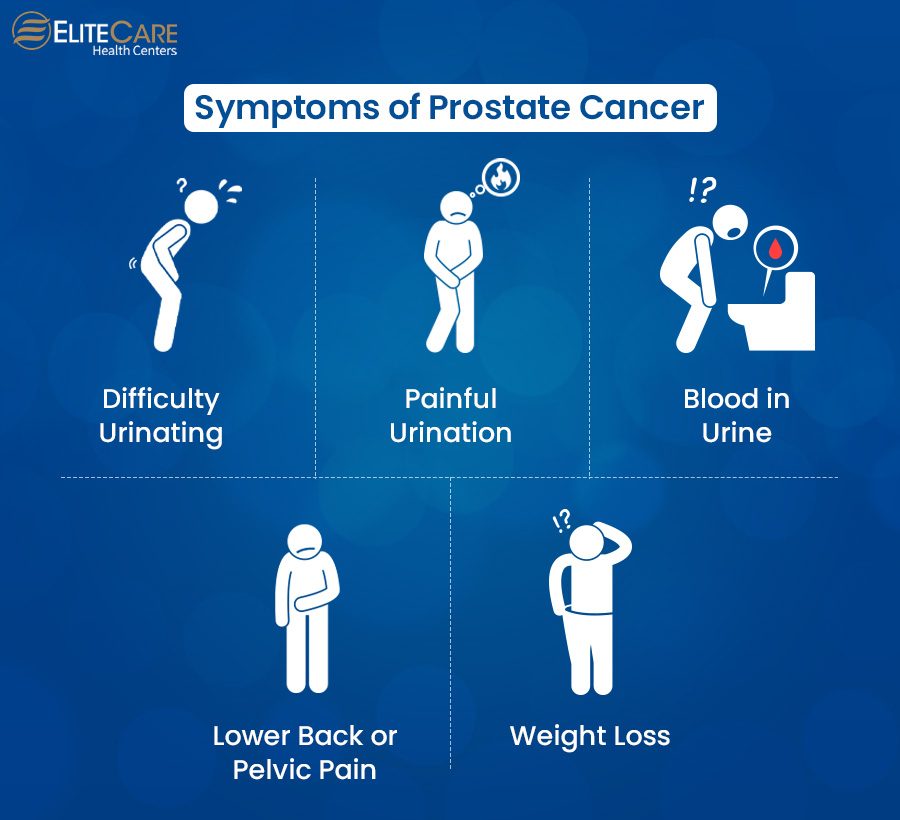
There are various warning signs and symptoms of prostate cancer. Here are a few:
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain during urination
- Blood in urine
- Lower back or pelvic pain
- Unexplained weight loss
What is Screening and How Does it Help Detect Prostate Cancer Early?
Screening is a form of preventative health care in which patients are tested for a particular disease or condition before the symptoms appear. The aim of screening is to detect diseases or conditions early when they are most treatable. For some types of cancer, prostate cancer, for example, early detection can lead to an excellent prognosis. Screening for prostate cancer can help find tumors that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated promptly.
Prostate cancer is relatively slow growing. It may take several years for it to reach a detectable size and even longer for it to metastasize to other organs. It is possible to live a healthy life with prostate cancer so long as it is carefully monitored to track for any unusual changes or abnormal growths. But in some cases, immediate treatment might be needed if the cancer is growing aggressively or is at risk of spreading.
Screening for prostate cancer usually involves a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. During this procedure, a tiny sample of blood is collected from the arm and the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate, is measured. This test can help detect and manage the symptoms of prostate cancer better.
Another way to find prostate cancer is through a digital rectal exam (DRE). In DRE, a physician inserts a gloved lubricated finger into the rectum of the patient to feel the prostate gland. If the results for either of these tests turn out to be abnormal then a prostate biopsy may be required to ascertain whether the patient is suffering from cancer.
Screening can not only help detect cancer early but can also determine whether immediate treatment is necessary. It can help distinguish between slow-growing and aggressive cancers and help plan a course of action accordingly.
What Age Should Men Get Screened for Prostate Cancer?
Men with a family history of the prostate, pancreas, or other cancers are recommended to get screened for prostate cancer from the age of 40. Similarly, men of African American descent or men with known BRCA mutations must start getting screenings at the age of 40. As for men who are not African American and have no family history of cancer, the recommended age to start getting screenings is 45.
Men between the age of 55 and 69 can choose to undergo a screening at any time and should consult a physician to discuss the same. However, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force strongly recommends against screenings for men aged 70 and older. After the age of 70, the risks of screening outweigh the potential benefits as they are more likely to have other health issues that make them more vulnerable to the risks associated with the medical procedure.
Conclusion
In the United States, 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetime; and 1 in 41 men will succumb to this illness. While the risk of mortality due to prostate cancer is quite high, preventative measures like screening and active surveillance can improve the odds of beating this illness. If you are at risk for prostate cancer, consult your physician to discuss the best course of action.
For routine check-ups or screenings visit the nearest EliteCare clinic or visit their website to schedule an appointment.






