
Although pharmaceuticals are helpful in the management of hypertension, dietary and lifestyle modifications are the most effective ways to naturally control blood pressure and lower the risk of related health issues.
The Importance of Managing Blood Pressure
It’s important to understand why controlling blood pressure is so important for general health and well-being. The force of blood against your artery walls as your heart pumps blood throughout your body is measured by blood pressure.
When this force is continuously too strong, it can harm the organs and arteries over time, resulting in a variety of health issues, such as:
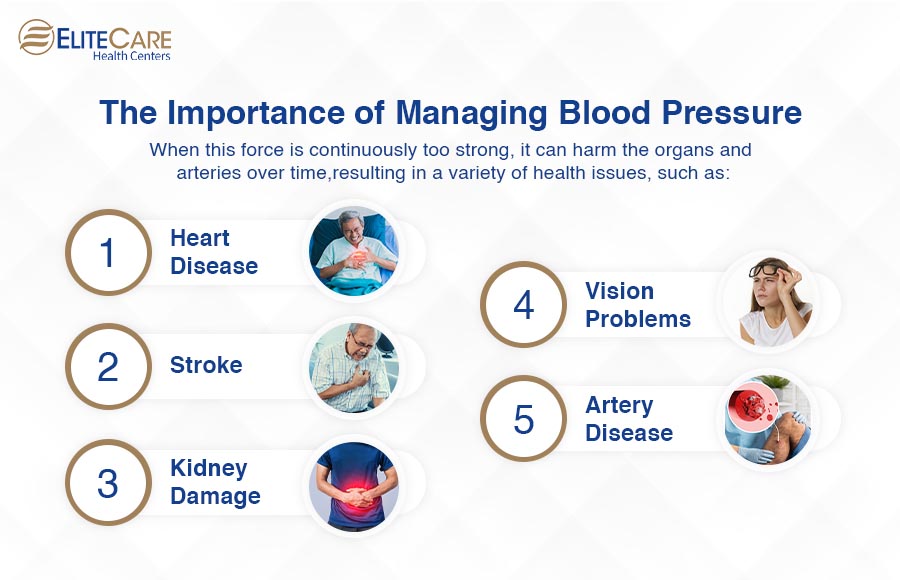
- Heart Disease
- Stroke
- Kidney Damage
- Vision problems or even blindness.
- Peripheral Artery Disease
Given these serious health risks, managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications, is essential for reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Diet to Lower High Blood Pressure
Several dietary patterns have been shown to effectively lower blood pressure, with an emphasis on consuming nutrient-rich foods while limiting or avoiding those high in sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars. There are many foods to lower blood pressure that you can opt for in your diet.
Here are key dietary recommendations for lowering high blood pressure:
1. The DASH Diet
The DASH diet, developed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), is specifically designed to lower blood pressure through dietary changes.
DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension and emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products while minimizing saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Key components of the DASH diet include:
- Fruits and Vegetables:
4–5 servings of fruits and vegetables should be your daily goal. These supply vital vitamins, minerals, and fiber that promote general well-being and reduce blood pressure.
- Whole Grains:
Choose whole grains over refined grains, such as quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats. Whole grains are high in minerals and fiber, which can help control blood pressure.
- Lean Proteins:
One of the best foods to lower blood pressure is lean protein sources such as fish, chicken, beans, and lentils. These proteins support the maintenance of normal blood pressure levels as they contain less saturated fat compared to red meat.
- Low-Fat Dairy:
Include low-fat or fat-free dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese in your diet for calcium and protein without the saturated fat found in full-fat dairy.
- Nuts, Seeds, and Legumes:
Incorporate nuts, seeds, and legumes like almonds, sunflower seeds, and lentils into your meals and snacks for heart-healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Limit Sodium:
Reduce sodium intake by choosing fresh or minimally processed foods and avoiding high-sodium processed foods such as canned soups, packaged snacks, and processed meats.
- Limit Added Sugars:
Minimize consumption of sugary beverages, desserts, and processed foods high in added sugars, as excessive sugar intake can contribute to high blood pressure and other health problems.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption:
If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limiting alcohol intake can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Portion Control:
Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can contribute to weight gain and hypertension.
2. Mediterranean Diet
Another dietary pattern linked to lower blood pressure and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease is the Mediterranean diet. This diet places less emphasis on processed foods and red meat and more on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, nuts, seeds, legumes, fish, and moderate amounts of poultry, eggs, and dairy products.
Key components of the Mediterranean diet include:
- Plant-Based Foods: Make fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes the foundation of your meals.
- Healthy Fats: Prioritize sources of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which provide omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health.
- Lean Proteins: Include moderate amounts of poultry, eggs, and dairy products, focusing on lean and low-fat options.
- Herbs and Spices: Flavor dishes with herbs and spices instead of salt to enhance taste without increasing sodium intake.
- Red Wine (in moderation): Moderate consumption of red wine, typically one glass per day for women and up to two glasses per day for men, is a characteristic feature of the Mediterranean diet and may offer cardiovascular benefits when consumed responsibly.
3. Vegetarian or Plant-Based Diet
A diet that excludes or limits animal products, such as vegetarianism or plant-based diets, has been linked with foods to lower blood pressure. Diets based mostly on plants are inherently low in cholesterol and saturated fats.
Guide to Low Sodium Eating
In addition to following a heart-healthy dietary pattern like the DASH diet, reducing sodium intake is crucial for managing blood pressure. Excess sodium can cause the body to retain water, leading to increased blood volume and elevated blood pressure. It’s important to follow a healthy lifestyle plan to maintain overall well-being.
Here are practical tips for adopting a low-sodium eating pattern:

1. Read Food Labels:
Pay attention to the sodium content listed on nutrition labels when shopping for packaged and processed foods. Choose products labeled “low sodium” or “no added salt” whenever possible.
2. Cook at Home:
Prepare meals at home using fresh, whole ingredients rather than relying on pre-packaged or restaurant meals, which are often high in sodium.
3. Flavor with Herbs and Spices:
Use herbs, spices, citrus juice, vinegar, and other flavorings to season your meals instead of salt. Experiment with garlic, ginger, rosemary, thyme, cumin, turmeric, and other aromatic ingredients to enhance the taste of your dishes.
4. Limit Processed Foods:
Minimize consumption of processed and convenience foods such as canned soups, frozen meals, packaged snacks, and fast food, which tend to be high in sodium.
5. Rinse Canned Foods:
If using canned beans, vegetables, or other canned goods, drain and rinse them under cold water to remove excess sodium.
6. Choose Fresh or Frozen Produce:
Opt for fresh or frozen fruits and vegetables over canned varieties, which often contain added salt for preservation.
7. Be Mindful When Eating Out:
When dining out, ask for sauces, dressings, and condiments on the side, and request dishes to be prepared without added salt. Choose restaurants that offer lower-sodium options or specialize in fresh, healthy cuisine.
8. Gradually Reduce Sodium Intake:
Gradually reduce the amount of salt you add to your meals to allow your taste buds to adjust to lower sodium levels over time.
Dietary changes that lower blood pressure are a potent and successful method of lowering cardiovascular disease risk and enhancing general health. You can maintain healthy blood pressure levels and reduce your risk of problems from hypertension by limiting your salt intake and adopting a heart-healthy eating pattern. Keep a list of foods to lower blood pressure as it will help you stay on track.
Connect with a primary care doctor to learn more about the kind of diet you should be following. Our health experts at EliteCare Health Centers can help you prepare a personalized meal plan as per your needs to lower your blood pressure. Visit our website or call +1-888-596-2090 for an appointment.
Frequently Asked Questions
High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. If left untreated, hypertension can lead to serious health complications.
Diet plays a significant role in blood pressure regulation. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting sodium and added sugars can help lower blood pressure naturally.
Yes, alcohol consumption can influence blood pressure levels. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking can increase blood pressure.





