As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes, and one critical aspect of health that can be significantly affected in seniors is the coagulation system – the body’s ability to form blood clots. Coagulation defects, or clotting disorders, can become increasingly prevalent as individuals age. Understanding the significance of coagulation defects is vital because they can have serious consequences. In this blog post, we will dig into the world of coagulation defects in seniors, unfolding their symptoms, causes, and available treatments.
What Are Coagulation Defects?
Coagulation defects, also known as clotting disorders, are medical conditions that hinder the body’s ability to form blood clots effectively. Blood clotting is a natural process that prevents excessive bleeding when we get injured. It plays a vital role for seniors in maintaining their overall health and well-being. Any disruptions in this process, as seen in coagulation defects, can lead to complications that may necessitate medical attention from medical clinics and health care centers.
Why is this topic important to discuss? Well, the aging population is expanding rapidly worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, by 2030, the global population aged 60 and over is expected to nearly double, reaching approximately 2.1 billion. With this demographic shift, understanding and addressing health issues specific to seniors, including coagulation defects, becomes paramount.
This coagulation system involves various factors and pathways. Understanding these components helps seniors and their caregivers recognize symptoms and aids healthcare clinics in providing appropriate diagnostic and treatment services.
Symptoms of Coagulation Defects in Seniors
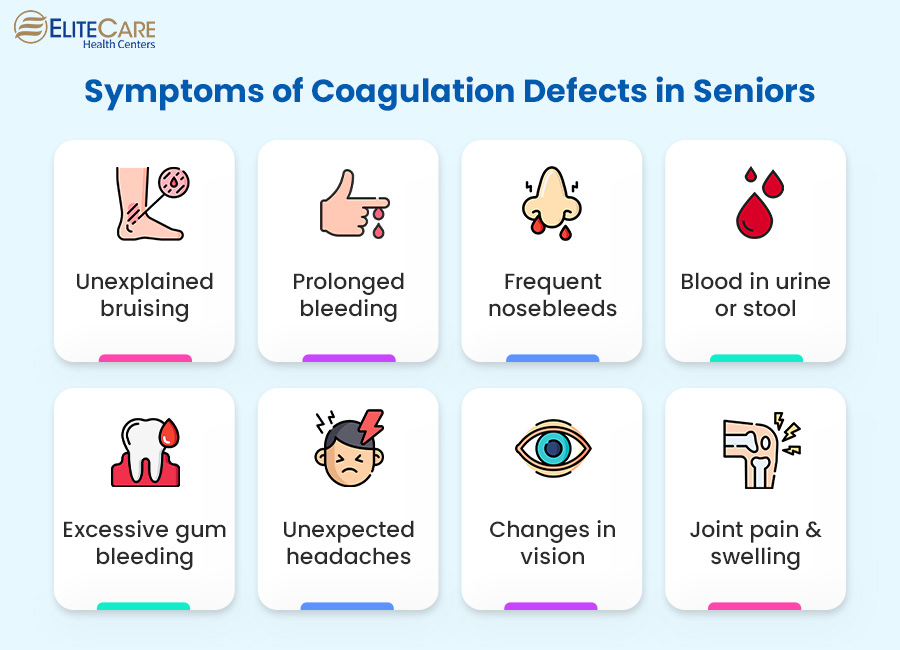
Coagulation defects can manifest through various symptoms, many of which may serve as crucial warning signs. These symptoms include but are not limited to:
- Unexplained and persistent bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or injuries
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Blood in urine or stool
- Excessive gum bleeding, especially after brushing or flossing
- Unexpected and severe headaches
- Changes in vision
- Joint pain and swelling
How These Symptoms Manifest in Older Adults
Coagulation defect symptoms may present differently in older adults due to the complex interplay of aging-related factors, medications, and cognitive changes. Here are some specific examples:
- Age-Related Joint Pain: Older adults often experience joint pain as a natural part of aging. This discomfort can make distinguishing between typical age-related common issues and pain related to coagulation defects challenging. For instance, a senior may dismiss joint pain, assuming it’s merely arthritis when it might be a symptom of a coagulation problem.
- Medications & Bleeding Risk: Many seniors take medications like blood thinners to manage other health conditions, such as heart disease or stroke prevention. While these medications are essential, they can increase the risk of bleeding events. This heightened bleeding risk can exacerbate coagulation defect symptoms, making them more pronounced or frequent. Thus, it’s crucial for healthcare providers in Elite Health and Wellness to carefully manage medication regimens for seniors, considering their potential impact on coagulation.
- Cognitive Decline: Cognitive decline is common in older adults, and it can affect their ability to recognize, remember, and communicate symptoms accurately. Seniors with cognitive impairment may have difficulty reporting symptoms or understanding their significance. This underscores the importance of caregivers and healthcare professionals in primary care centers being attentive to subtle changes and proactive in monitoring senior patients for coagulation defects.
By highlighting these complexities, we emphasize that coagulation defect symptoms in seniors may only sometimes present straightforwardly, making early detection and specialized care more critical for this age group.
Causes and Risk Factors
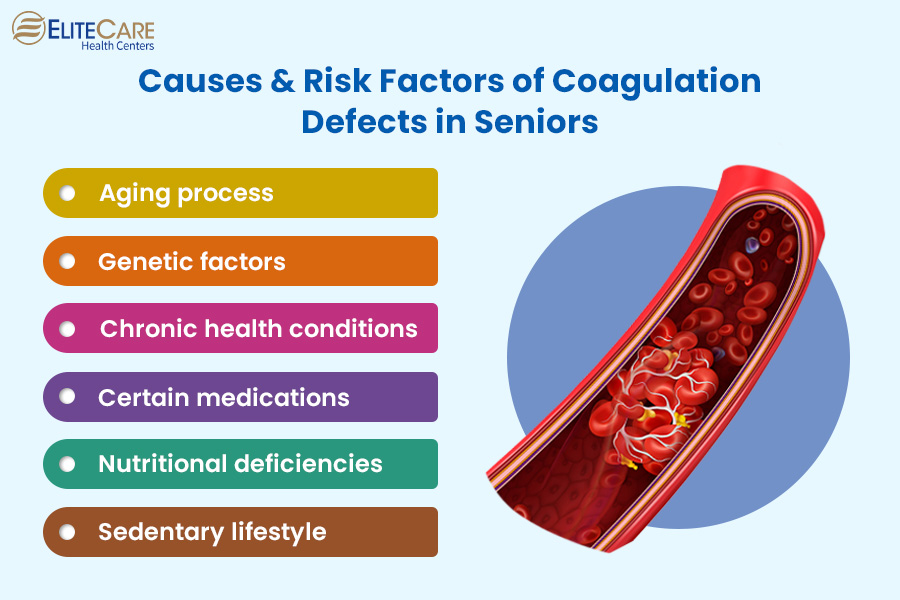
Primary Causes of Coagulation Defects in Seniors
Coagulation defects in seniors can have various primary causes, including:
- Age-Related Changes: With age, blood vessels become less elastic, and platelet function may decline, increasing the risk of coagulation defects.
- Genetic Factors: In some cases, coagulation defects can be hereditary. These genetic factors may become more pronounced with age.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Certain chronic illnesses common in seniors, such as liver and kidney disease, can directly impact the coagulation process, potentially leading to defects.
How Aging Affects Coagulation
- Reduced Platelet Function: With age, platelets, the blood cells responsible for clot formation, may become less responsive. This decreased platelet function can prolong bleeding.
- Vessel Changes: Aging blood vessels may become more fragile and prone to damage, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Other Contributing Factors
- Medications: Some medications prescribed to seniors, such as anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, can impact coagulation. Healthcare providers in nearby healthcare centers must carefully manage these medications to minimize the risk of coagulation defects.
- Diet and Nutrition: Poor nutrition and deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals (e.g., vitamin K) can affect blood clotting. Seniors should maintain a balanced diet to support healthy coagulation.
- Physical Activity and Lifestyle: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to coagulation issues, as physical activity helps maintain circulation and overall cardiovascular health.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Accurate diagnosis of coagulation defects in seniors is essential for effective management and care. Common diagnostic procedures and tests are as follows:
Blood Tests
Specific blood tests, such as prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and platelet count, can provide valuable information about the coagulation system’s functionality.
Coagulation Factor Assays
These tests measure the levels and activity of various clotting factors in the blood to identify deficiencies or abnormalities.
Bleeding Time Test
This test assesses how long it takes for a person’s blood to clot, providing insights into potential coagulation defects.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can identify hereditary coagulation disorders when a genetic component is suspected.
Imaging Studies
In some instances, imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans may be performed to visualize blood vessels and identify clot-related issues.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection enables timely intervention, reducing seniors’ risk of severe bleeding events and complications. This proactive approach improves quality of life through personalized care, including lifestyle adjustments and medications when needed.
Furthermore, it helps prevent life-threatening complications like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Seniors receive the specialized care they need by emphasizing routine physical exams, including blood tests, at medical centers or through online doctor consultations.
Treatment Options
Coagulation defects in seniors can be managed effectively through a combination of treatment approaches, such as:
Medications
Depending on the specific coagulation disorder, seniors may require medications such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), clotting factor concentrates, or platelet enhancers to regulate their blood clotting processes.
Blood Transfusions
In severe cases, blood transfusions may be necessary to replenish clotting factors or platelets.
Surgical Interventions
In some instances, surgical procedures or interventions may be recommended to address underlying causes or complications related to coagulation defects.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes play a key role in managing coagulation defects. Seniors should be educated about avoiding activities that may increase the risk of bleeding and encouraged to adopt a balanced diet and maintain regular physical activity to support overall health.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Routine or annual physical exams and blood tests are crucial for monitoring treatment effectiveness and making necessary adjustments.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatments are tailored to each individual’s unique needs, reducing risks and optimizing their quality of life. Personalization ensures seniors receive the most appropriate care and encourages treatment adherence, leading to better outcomes. In managing coagulation defects, the collaborative approach of discussing various treatment options and emphasizing personalized care plans with their primary care physician at EliteCare Medical Centers is vital for seniors’ well-being and preventing complications.
To Sum Up
EliteCare Health Centers offers specialized senior care services that prioritize the well-being of elderly loved ones. Through comprehensive care plans, routine medical check-ups, and access to a team of experienced healthcare professionals, Elite Health Care plays a pivotal role in addressing the unique healthcare needs of seniors.
If you, or someone you care for, suspects the presence of coagulation defects, we urge you not to delay seeking medical advice. Prompt consultation with healthcare providers, whether through EliteCare Health Center’s services or elsewhere, can make a profound difference in managing coagulation disorders and ensuring a healthier, more vibrant future for the beloved seniors.