One of the significant challenges seniors face is age-related muscle loss. Also known as sarcopenia, this refers to the gradual decline in muscle mass, strength, and function with advancing age. Muscles are the powerhouses of our bodies, providing the strength and stability we need to perform everyday activities and pursue our passions.
Unfortunately, with age, the gradual decline in muscle mass and function can lead to reduced mobility, increased frailty, and a higher risk of falls and injuries. With the right knowledge and a proactive approach, we can effectively combat age-related muscle loss and live vibrant and fulfilling lives.
What Causes Age-Related Muscle Loss?
Age-related muscle loss, or sarcopenia, is a complex process influenced by multiple factors. Understanding the science behind this condition can help one to develop effective strategies to prevent or manage it.
Sarcopenia is the gradual and progressive decline in muscle mass, strength, and function that typically begins around 30. As we age, several key factors play a significant role in the development of this condition, such as:
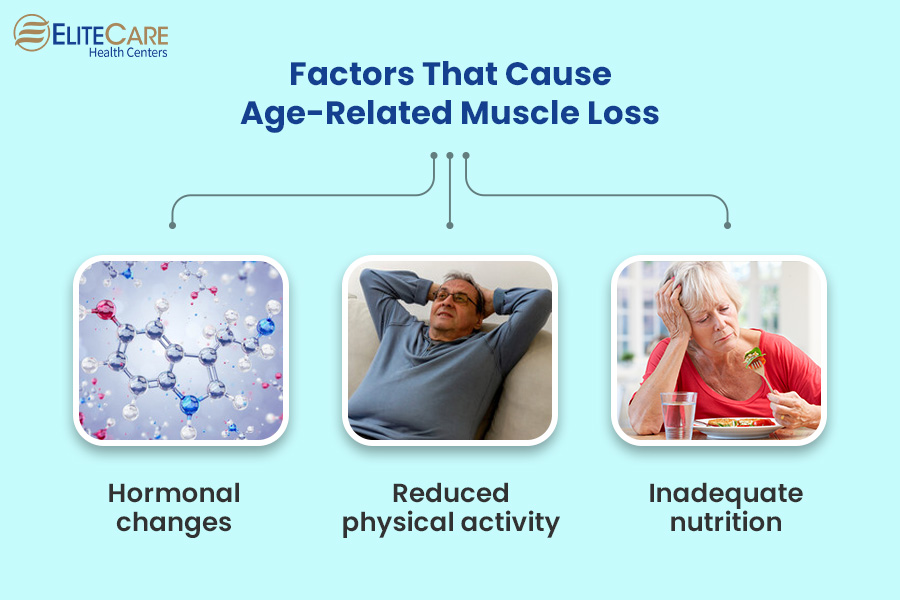
Hormonal changes – A decrease in growth hormone and testosterone levels can contribute to the loss of muscle tissue. These hormonal shifts affect muscle protein synthesis, making it more challenging for the body to maintain and repair muscle fibers.
Reduced physical activity – With age, activity levels decline, and the muscles experience less stimulus, decreasing muscle mass and strength over time.
Inadequate nutrition – With increasing age, the bodies become less efficient at absorbing and utilizing essential nutrients like protein. Since protein is the building block of muscles, insufficient intake can hinder muscle repair and maintenance.
Signs and Symptoms
- Gradual reduction in muscle mass
- Reduced muscle strength
- Decreased endurance and stamina
- Impaired balance and coordination
- Slower recovery from injuries
- Changes in gait and mobility
Early detection and intervention are essential to prevent further muscle decline and preserve functional abilities. By recognizing the signs and symptoms mentioned above, individuals can consult with healthcare clinic professionals, such as primary care physicians, physical therapists, or registered dietitians, to develop personalized strategies to combat age-related muscle loss.
Interventions may include resistance training exercises to build strength and muscle mass, nutritional adjustments to support muscle health, and lifestyle modifications to enhance overall physical activity levels. Monitoring muscle mass, strength, and functional abilities can also help track progress and guide intervention strategies.
Risk Factors for Age-Related Muscle Loss
By understanding risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their impact and preserve muscle mass and function.
1. Sedentary lifestyle
Leading a sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of inactivity and minimal physical exercise, is a significant risk factor for muscle loss. When muscles are not regularly engaged through physical activity and exercise, they experience disuse and gradually weaken over time.
2. Inadequate nutrition
Poor nutrition, specifically inadequate protein intake, can increase the risk of muscle loss. A diet lacking essential muscle maintenance and repair nutrients can hinder muscle protein synthesis, leading to muscle wasting.
3. Chronic illnesses
Certain chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cancer can impact muscle health and contribute to muscle wasting.
4. Medications
Some medications can contribute to muscle loss as a side effect. For instance, long-term use of corticosteroids, commonly prescribed for conditions like asthma or rheumatoid arthritis, can lead to muscle wasting.
5. Hormonal changes
Hormonal imbalances associated with aging, such as a decline in testosterone, growth hormone, and IGF-1, can contribute to muscle loss. These hormones are critical in muscle growth, repair, and maintenance.
6. Genetic factors
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to experience accelerated muscle loss with age.
Medical clinics, health care centers, and senior care services can provide comprehensive assessments, personalized interventions, and ongoing support to address these risk factors and preserve muscle mass in older adults.
Preventive Measures for Age-Related Muscle Loss

Preventive measures are crucial to minimize age-related muscle loss and maintain muscle mass as one ages. Implementing certain lifestyle changes and incorporating specific strategies can effectively promote muscle health and preserve functional abilities. Some practical ways and recommendations are as follows:
1. Regular exercise
Being physically active is essential for maintaining muscle health, especially for seniors. Engaging in regular exercise can provide numerous benefits. For seniors, it is important to focus on exercises that are safe and appropriate for their age and fitness level. Incorporating exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling can improve cardiovascular fitness and overall endurance.
Additionally, strength training exercises using light weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises can help maintain and build muscle mass. Balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or practicing yoga, can enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or a certified trainer to design an exercise program tailored to seniors’ specific needs and abilities.
2. Proper nutrition
To support muscle maintenance and repair, one should consume sufficient protein from lean sources such as meats, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy, legumes, and tofu. Including essential nutrients like vitamins D, E, and C and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium in the balanced diet helps promote muscle function and recovery. Keep the body hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
3. Lifestyle modifications
Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity and incorporate physical activity into your daily routine. One should take regular breaks from sitting and engage in light exercises or stretching.
Additionally, managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or activities that promote relaxation, as chronic stress can negatively impact muscle health. Prioritize sufficient sleep of 7-9 hours per night, as it is crucial for muscle repair, recovery, and overall health. One can support muscles and promote optimal well-being by implementing these lifestyle changes.
4. Seek professional guidance
Prioritizing preventive care and seeking regular consultations with our healthcare center professionals is crucial in maintaining muscle health. Through routine check-ups, online doctor consultations, or visits to healthcare clinics, underlying health issues contributing to muscle loss can be identified early on, allowing for timely intervention.
It is also important to discuss any medications one is taking with a healthcare provider to understand potential side effects that could impact muscle health. Exploring alternative options when appropriate ensures a comprehensive approach to preserving the muscles and optimizing overall well-being.
To Sum Up
Don’t wait until muscle loss becomes a significant concern. Take charge of your muscle health today. Connect with our professionals at Elite Care Health Centers for comprehensive care. Our team of healthcare professionals offers services such as healthcare clinic visits and routine and annual physical exams. Through these services, we can assess your muscle health, identify any underlying issues, and develop personalized strategies to preserve and strengthen your muscles.
It’s never too late to start. Take the first step towards prioritizing your muscle health and unlock a brighter, healthier future. Muscles are the foundation of mobility and strength, so invest in them and embrace the joy of an active and vibrant life as you age.