Fractures are a serious concern for older adults, posing challenges to their health and independence. With age, our bones become more vulnerable to fractures, necessitating a focused approach to recovery. Taking appropriate steps and embracing self-care is pivotal for older adults to navigate the recovery process successfully and regain their quality of life.
The increased risk of broken bones in older adults can be attributed to several factors. Age-related changes impact bone density and strength, resulting in conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis, making bones more susceptible to fractures. Additionally, age-related declines in balance, muscle strength, and reflexes contribute to a higher likelihood of falls, a common cause of fractures in this population.
The increased risk of fractures in older adults can be attributed to various factors.
This blog post will explore the steps older adults should take after experiencing a broken bone. From immediate actions to long-term rehabilitation and preventive measures, we will provide valuable insights to support older adults in their recovery and help them regain independence and a higher quality of life.
Recognizing Broken Bone Symptoms
If one suspects a broken bone, be aware of common symptoms such as intense pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, difficulty moving the affected area, or a snapping sound at the time of injury. These indicators suggest the need for prompt attention and medical evaluation.
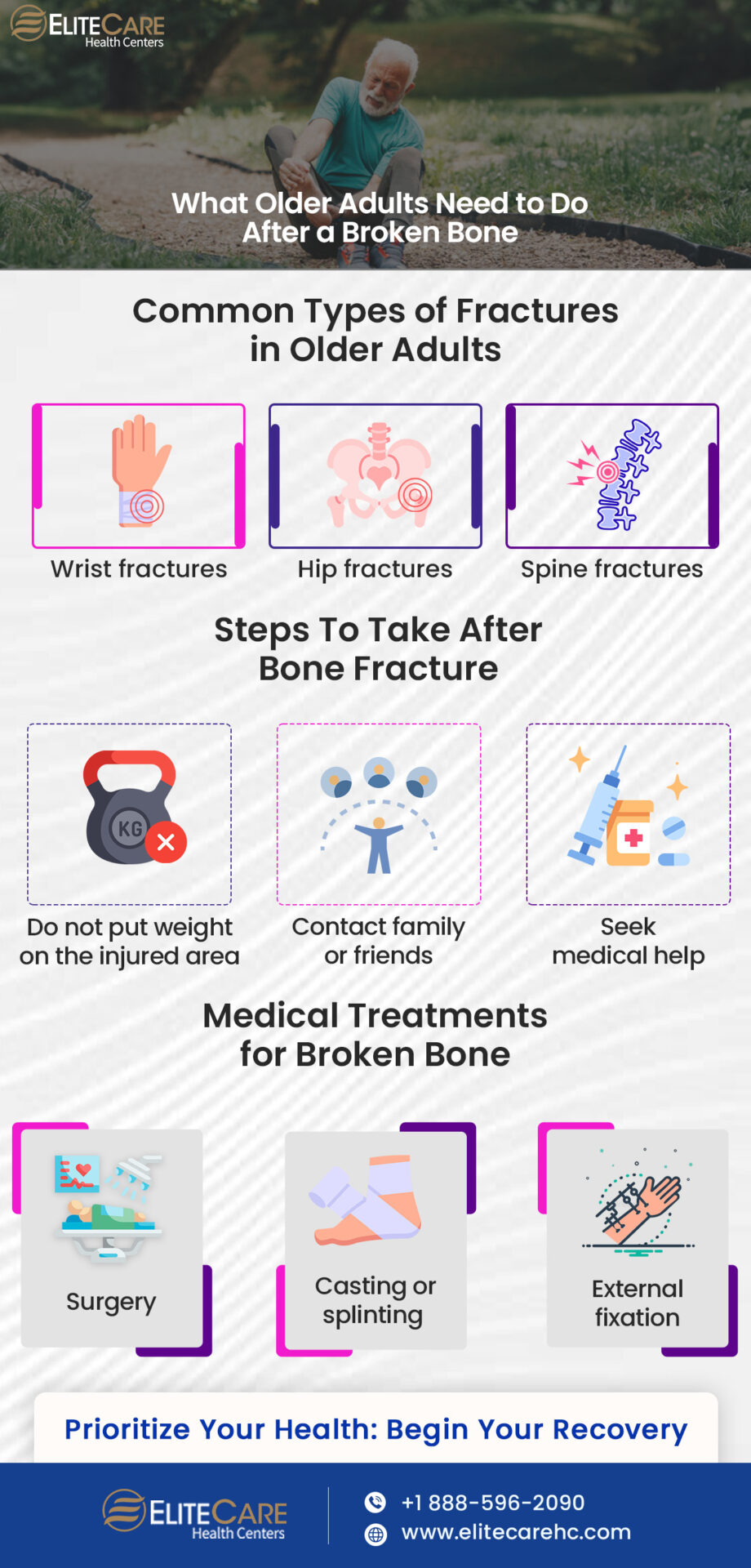
Types of Fractures Common in Older Adults
1. Wrist Fractures
Fractures in the wrist, particularly of the distal radius (a bone in the forearm), are prevalent in older adults. These fractures are commonly caused by falls, especially when individuals instinctively use their hands to break their fall. Wrist fractures can impact daily activities and hand function.
2. Hip Fractures
3. Spine Fractures (Vertebral Compression Fractures)
Older adults with osteoporosis are susceptible to vertebral compression fractures, which can occur spontaneously or due to minimal trauma, such as bending or lifting. These fractures can lead to chronic back pain, loss of height, and changes in posture.
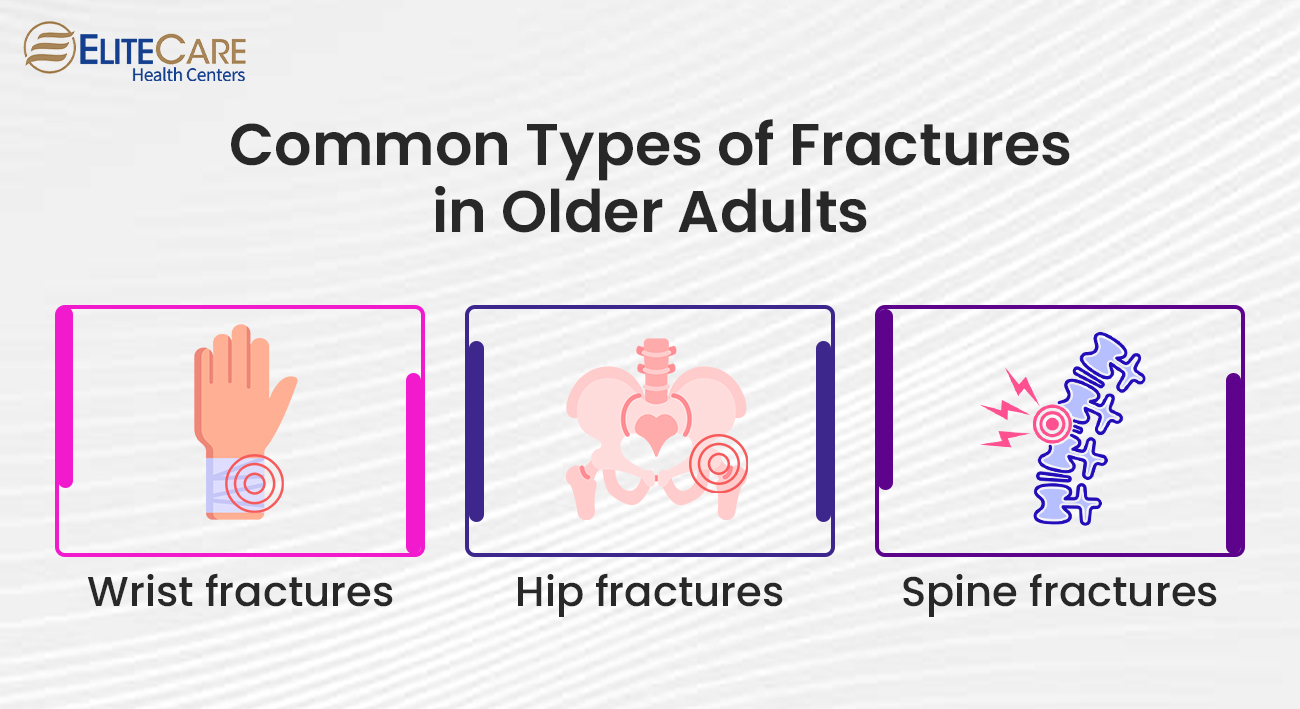
Immediate Steps to Take
Experiencing a broken bone can be a distressing situation. Taking immediate and appropriate actions after sustaining a fracture is crucial for minimizing further damage and facilitating healing. Here are the key steps to follow:
1. Do Not Put Weight on the Injured Area and Immobilize It
When a broken bone is suspected, avoiding weighting the injured area is important. Do not attempt to move or straighten the bone yourself, as this may worsen the injury. Instead, take the following steps:
a) Stay Still: If possible, keep the injured area as still as possible to prevent further damage.
b) Immobilize the Fractured Area: Gently immobilize the fractured area using a splint, towel, or any available rigid material.
c) Elevate the Injured Limb: If possible, elevate the injured limb slightly above heart level to help reduce swelling.
2. Seek Medical Help Immediately and Call for Assistance
After immobilizing the injured area, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Here’s what you should do:
a) Contact Doctor: Contact your family doctor or the nearest medical clinic to explain the situation. They can guide the next steps to help seniors with fractures.
b) Call for Assistance: If the pain is severe or if the senior is unable to move independently, call for assistance from a family member, neighbor, or emergency services. They can help older adults to reach primary care physicians or health care centers safely.
3. Importance of Seeking Medical Help
Seeking medical attention promptly is crucial for several reasons, such as follows:
a) Accurate Diagnosis: A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the fracture and determine the appropriate treatment plan based on the severity, location, and fracture type.
b) Pain Management: Healthcare providers can provide pain management strategies, such as medication or local anesthetics, to alleviate discomfort during the initial stages.
c) Preventing Complications: Early medical intervention helps prevent complications like infection, improper healing, or long-term functional impairments.
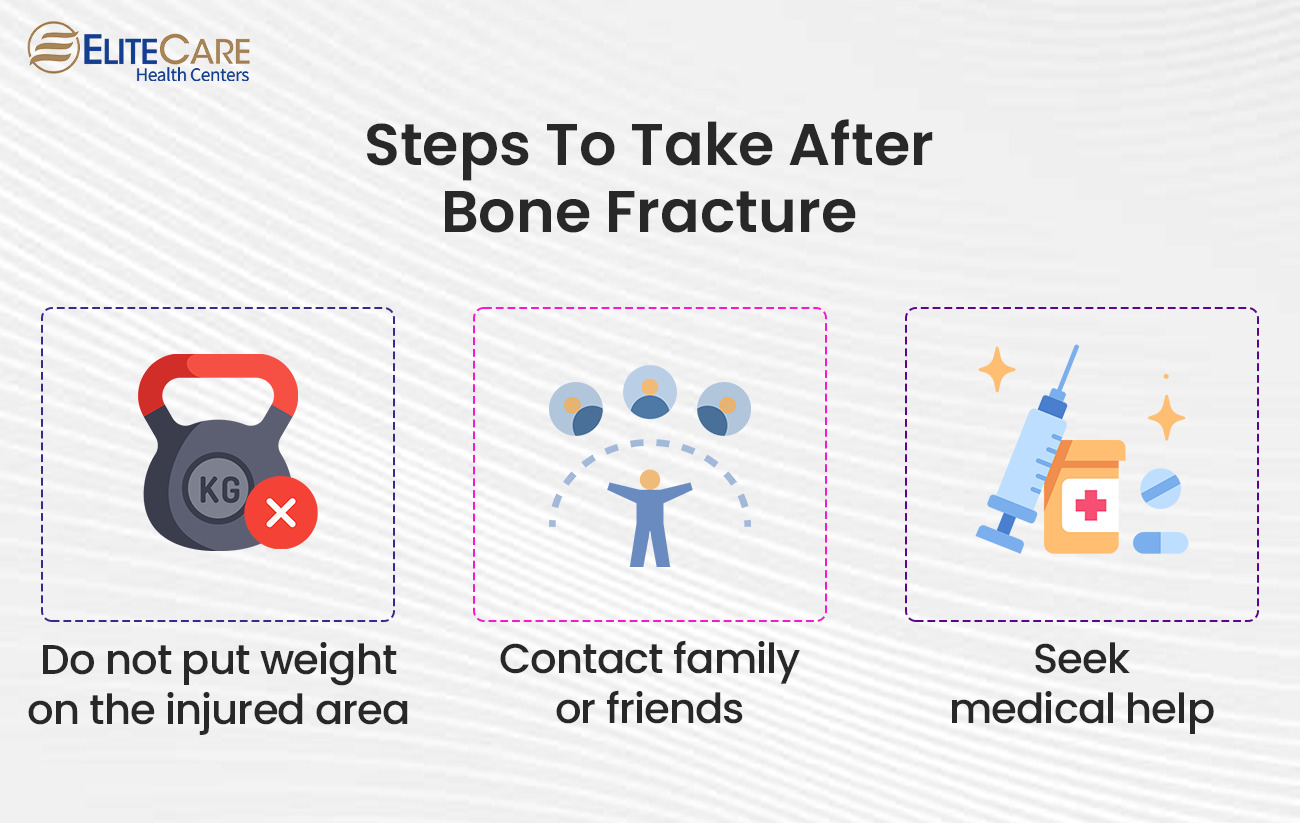
Medical Treatment and Recovery
After a broken bone diagnosis, medical interventions and treatments are crucial in promoting healing and restoring functionality for older adults. The specific approach will depend on the severity and type of fracture and individual circumstances. Typical medical interventions and treatments for broken bones in older adults are as follows:
1. Surgery
Surgery may be necessary in some cases, especially for more severe fractures or those involving hips and joints. Surgical interventions aim to realign broken bones and stabilize them using internal fixation (screws, plates, or rods) or joint replacement procedures. An orthopedic surgeon typically performs surgery and may require a hospital stay.
2. Casting or Splinting
Casting or splinting may be employed for fractures that do not require surgery. This involves applying a rigid or semi-rigid cast or splint to immobilize the broken bone, allowing it to heal in the correct position. Casting is commonly used for fractures in the extremities, such as wrists or ankles.
3. External Fixation
External fixation may be used in complex fractures or cases where the skin or soft tissues are severely injured. This technique involves using pins or screws placed externally to stabilize the bone fragments and facilitate healing.
4. Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain management is crucial in the treatment of broken bones. Healthcare providers employ various strategies to alleviate pain and discomfort. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or prescribed opioids may be used to manage pain, with the choice and duration determined by factors like pain severity and overall health. Apart from medications, local anesthetics, such as injections or nerve blocks, provide targeted pain relief by numbing the affected area. Physical modalities like heat or cold therapy, such as applying ice packs or warm compresses, can also help reduce pain and swelling, promoting healing. Following prescribed dosages and consulting healthcare providers through visits or online doctor consultations about potential side effects is important.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation is essential for maximizing the healing process and optimizing recovery outcomes. It offers numerous benefits, such as restoring mobility, strength, and functionality, enabling individuals to regain their independence, and helping to perform everyday tasks. Additionally, rehabilitation reduces the risk of muscle weakness, joint stiffness, and other limitations during the healing phase. Engaging in repair also supports psychological well-being, instilling confidence and providing control over the recovery process.
On the other hand, physical therapy is a key component of rehabilitation for broken bones. Physical therapy exercises are designed to restore mobility, rebuild strength, and enhance overall function. Range of motion exercises gradually increases joint mobility and flexibility. Strengthening exercises target the muscles surrounding the fractured area, promoting stability and efficient movement. Balance and coordination exercises improve equilibrium and proprioception, reducing the risk of falls. Additionally, functional training focuses on practicing tasks relevant to daily activities, empowering individuals to regain independence in actions like standing up from a chair or climbing stairs—falls and promoting overall stability.
Self-Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
During recovery, older adults can take proactive steps to manage their daily activities, promote independence, and ensure a smooth healing process. Implementing self-care strategies and making necessary lifestyle adjustments can significantly contribute to a successful recovery.
1. Managing Daily Activities
During the recovery period, older adults need to seek assistance from family, friends, or caregivers for tasks that may be challenging, including household chores, grocery shopping, or transportation to medical appointments. Modifying the home environment by removing tripping hazards, securing rugs, installing handrails in bathrooms and staircases, and ensuring proper lighting creates a safe and comfortable space for recovery. Additionally, assistive devices such as crutches, walkers, canes, or wheelchairs, as recommended by senior care service providers or primary care physicians, provide support, enhances mobility, and helps maintain balance during recovery.
2. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A nutritious diet is crucial for the recovery process. Ensure a well-balanced diet that includes calcium-rich dairy products, leafy greens, lean proteins, and fruits and vegetables to support healing and promote bone health. Consulting a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized dietary recommendations is recommended. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking adequate water throughout the day is important as sufficient hydration supports overall health, including optimal healing and proper body functioning. Insufficient rest and sleep are also essential for tissue repair and overall well-being. Prioritize rest and follow healthcare providers’ recommendations for positioning during sleep, using supportive pillows or cushions to ensure comfortable sleep and proper alignment.
By implementing these self-care strategies, utilizing assistive devices and modifications, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, older adults can actively support their recovery process, promote independence, and enhance their overall well-being. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals and follow their guidance for personalized recommendations and support during recovery.
The Bottom Line
To ensure a successful recovery, older adults must prioritize their healing process and follow the advice provided by EliteCare Health Centers healthcare professionals. Annual or routine physical exams can also help monitor overall health and address any concerns related to bone health. Furthermore, it is essential to emphasize the significance of taking preventive measures to reduce the risk of future fractures. By implementing the strategies mentioned in the blog post, older adults can proactively protect themselves and promote long-term well-being.