Medicare, the federal health insurance program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), plays a crucial role in providing healthcare coverage, including vital Medicare services, to seniors and individuals with disabilities in the United States.
As one explores the world of Medicare benefits, this comprehensive guide will shed light on its different sections, coverage options, eligibility criteria, enrollment process, costs, and Medicare advantages.
Whether one is approaching the age of eligibility or supporting a loved one, this guide equips them with the knowledge needed to navigate Medicare effectively. Read on to learn more.
Medicare Parts and Coverage
Medicare is divided into different parts, each providing specific coverage to meet various healthcare needs. Understanding these parts will help one grasp the extent of coverage offered by Medicare.
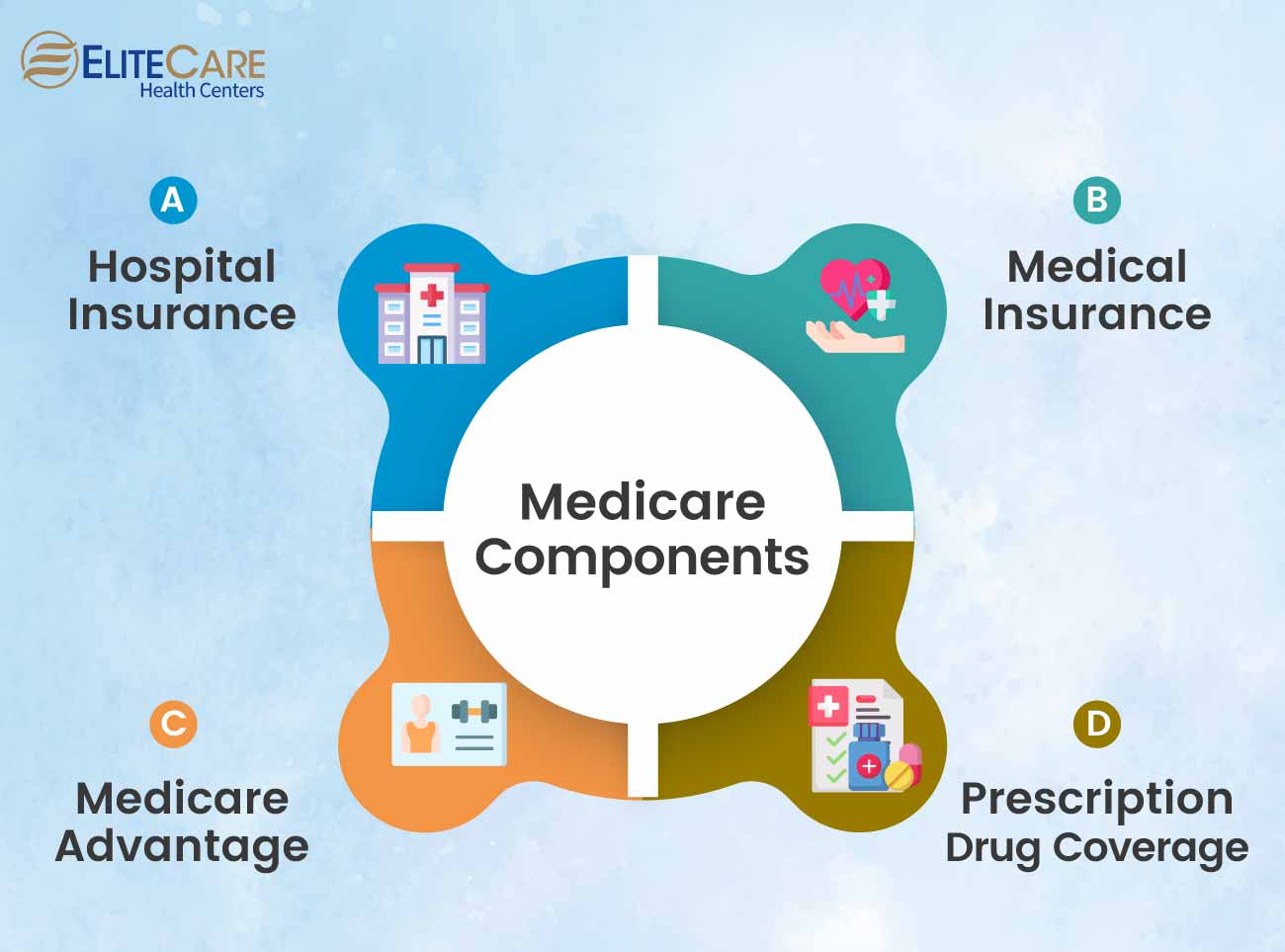
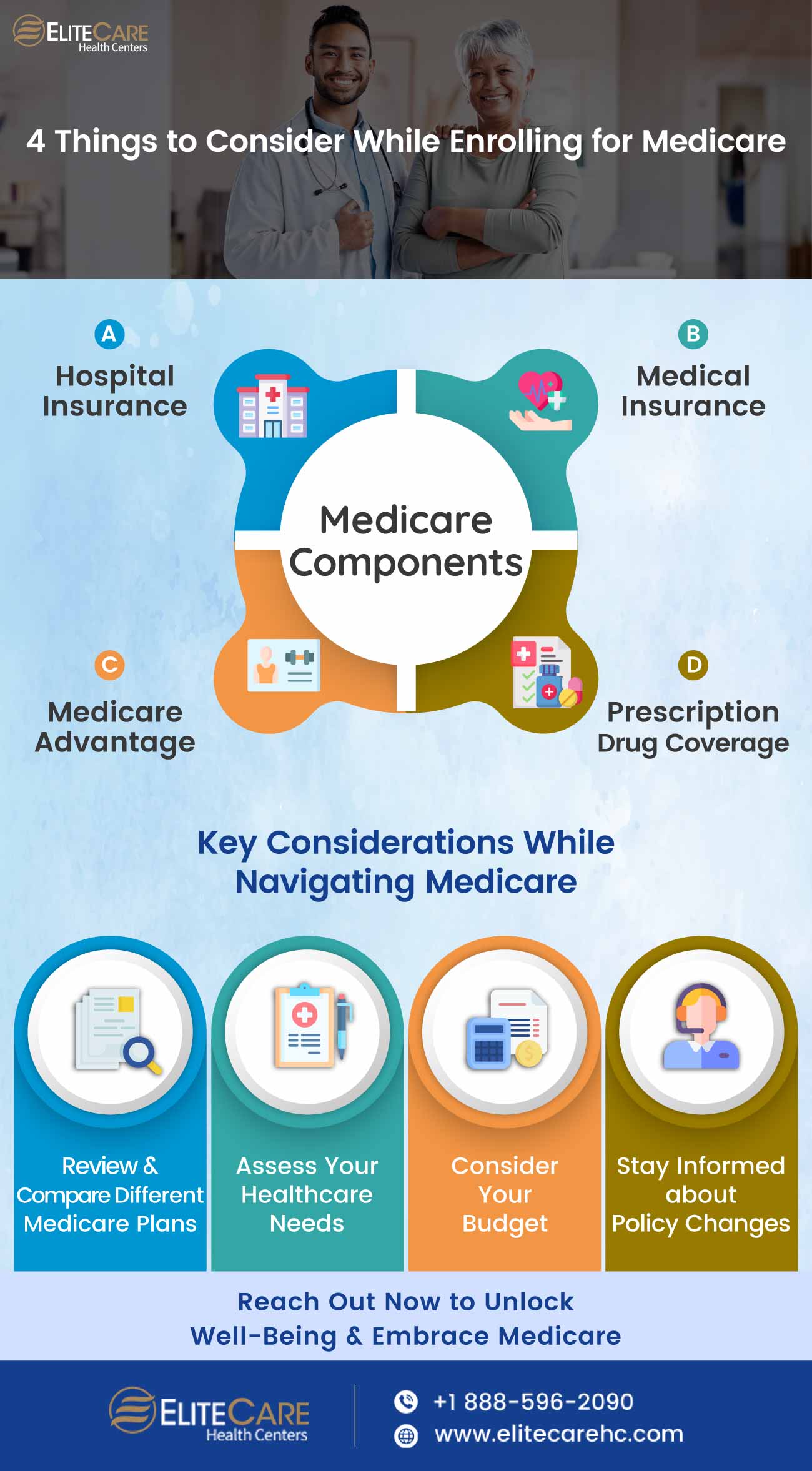
Part A: Hospital Insurance
- Covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and limited home health services.
Part B: Medical Insurance
- Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, preventive services, and medical supplies.
Part C: Medicare Advantage
- Offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare, Part C combines Parts A and B coverage, often with additional benefits like prescription drugs, dental, and vision.
Part D: Prescription Drug Coverage
- Stand-alone prescription drug plans that provide coverage for medications.
Eligibility and Enrollment
To access the benefits of Medicare, it’s essential to understand who qualifies and how to enroll. Let’s explore the eligibility criteria and enrollment process:
Who qualifies for Medicare?
- Individuals aged 65 and older: Most people become eligible for Medicare at age 65, regardless of their income or medical history.
- Individuals with certain disabilities: Younger individuals with specific disabilities, such as end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), may also qualify for Medicare.
Enrollment process
- Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): This is the first opportunity to enroll in Medicare, starting three months before one’s 65th birthday month and with this period lasting for another seven months.
- Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs): In certain situations, individuals may qualify for a SEP, allowing them to enroll or make changes outside the IEP. Examples include losing employer coverage or relocating.
- Annual Enrollment Period (AEP): During the Annual Enrollment Period, from October 15th to December 7th, Medicare beneficiaries can review and optimize coverage options for the coming year. Seek guidance from health care clinics to make informed decisions tailored to individual healthcare needs. Stay prepared and take charge of your well-being.
Understanding the eligibility criteria and enrollment process ensures timely access to Medicare benefits. Stay informed to make the most of Medicare and explore personalized care at a medical clinic, health care center, or with the guidance of your primary care physician.
Medicare Costs
Understanding the costs associated with Medicare is essential for managing one’s healthcare expenses. Here’s an overview of the different cost aspects:
Premiums
- Medicare Part A is generally premium-free for most beneficiaries who have paid Medicare taxes while working. This means one won’t have to pay a monthly premium to receive coverage for inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facilities, and some home health services.
- Part B requires a monthly premium, which can vary based on one’s income. Higher-income individuals may pay a higher premium amount. Part B premium covers services like doctor visits, preventive care, outpatient care, and durable medical equipment.
Deductibles and Coinsurance
- Medicare Part A has a deductible for hospital stays, which one must pay before Medicare coverage starts. The deductible amount can change each year. Once the deductible is met, Medicare covers the remaining hospital costs for a certain number of days.
- For extended hospital stays, Part A imposes coinsurance costs, where one shares the expenses with Medicare. After a certain number of covered days, one day be responsible for a portion of the daily coinsurance amount.
- Medicare Part B has an annual deductible that one must meet before Medicare starts paying its share. After the deductible is met, Medicare typically covers 80% of approved services, leaving one responsible for the remaining 20% as coinsurance. This includes doctor visits, outpatient therapy, durable medical equipment, and other outpatient services.
Copayments
- Medicare Part D, which covers prescription drugs, involves copayments or coinsurance for medications. The exact amount depends on the specific medications and one’s chosen Part D plan. Different drugs may have different cost tiers, and the copayment amounts can vary based on whether the drug is generic, brand-name, or a specialty medication.
- Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage) plans may have copayments for services. These amounts can vary based on the plan and the services one receives. Copayments may apply to doctor visits, specialist visits, hospital stays, and other covered services. Medicare Advantage plans often have different cost structures and may require copayments for each service received.
Financial Assistance
Medicare offers financial assistance programs for eligible individuals with limited income and resources.
- Medicare Savings Programs provide help with premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance. These programs are administered by one’s state and can help reduce one’s out-of-pocket costs for Medicare services. The specific eligibility requirements and benefits vary by state.
- The Low-Income Subsidy (Extra Help) assists with prescription drug costs, including premiums, deductibles, and copayments. This program helps individuals with limited income afford their prescription medications. Eligibility is based on income and resources, and the program can significantly reduce one’s out-of-pocket spending on prescription drugs.
Medicare Made Easy: Top 4 Considerations for Seniors
When it comes to navigating Medicare and making informed decisions about one’s healthcare coverage, there are several key considerations to keep in mind. Taking these factors into account can help one choose the most suitable Medicare plan for one’s specific needs. Here’s what one should consider:

1. Review and Compare Different Medicare Plans
- Medicare offers various options, including Original Medicare (Parts A and B), Medicare Advantage (Part C), and standalone prescription drug coverage (Part D). It’s essential to review and compare these plans to determine which one aligns best with one’s healthcare needs, budget, and preferred level of coverage.
- Consider factors such as monthly premiums, deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, provider networks, covered services, and prescription drug formularies. Evaluate how each plan addresses one’s specific healthcare requirements and whether it offers the flexibility and benefits that matter most.
2. Assess Healthcare Needs
- One should reflect on their current health status and any ongoing medical conditions or anticipated healthcare needs. Is one primarily concerned about hospital stays and major medical expenses (Part A)? Does one require regular doctor visits and preventive care (Part B)? Is one taking prescription medications (Part D)?
- Understanding one’s healthcare needs will help one prioritize the coverage elements that are most important to them. For example, if one frequently needs prescription medications, a plan with comprehensive Part D coverage may be a top consideration.
3. Consider the Budget
- Medicare costs can vary significantly depending on the type of plan one chooses. One should assess their budget and determine how much they can comfortably afford in terms of premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Remember to consider not only the immediate costs but also the potential long-term expenses. For instance, Medicare Advantage plans may offer lower monthly premiums but require higher copayments for certain services. One should analyze the expected healthcare utilization to estimate the overall cost implications of each plan.
4. Stay Informed about Policy Changes
- Medicare policies and coverage guidelines can change from year to year. It’s crucial to stay informed about any updates or modifications that may impact one’s coverage.
- Keep an eye on official Medicare communications, newsletters, and notices. One can also visit the official Medicare website or consult licensed insurance agents who specialize in Medicare to stay up to date with any policy changes, new benefits, or enrollment periods.
The Bottom Line
Medicare plays a vital role in providing healthcare coverage for seniors and individuals with disabilities. By understanding the different parts of Medicare, eligibility requirements, costs, and coverage options, one can make informed decisions to meet their healthcare needs. Remember to review and compare different Medicare plans, stay aware of policy changes, and seek assistance when needed.
Ready to embark on a proactive health journey? Discover the benefits of EliteCare Health Centers and experience personalized care tailored to unique needs. With a team of experienced professionals to guide you through Medicare options, rest assured of well-being and ongoing support. Embrace a stronger and healthier lifestyle in the golden years with EliteCare by your side. Reach out today to unlock the full potential of well-being and make the most of Medicare together.