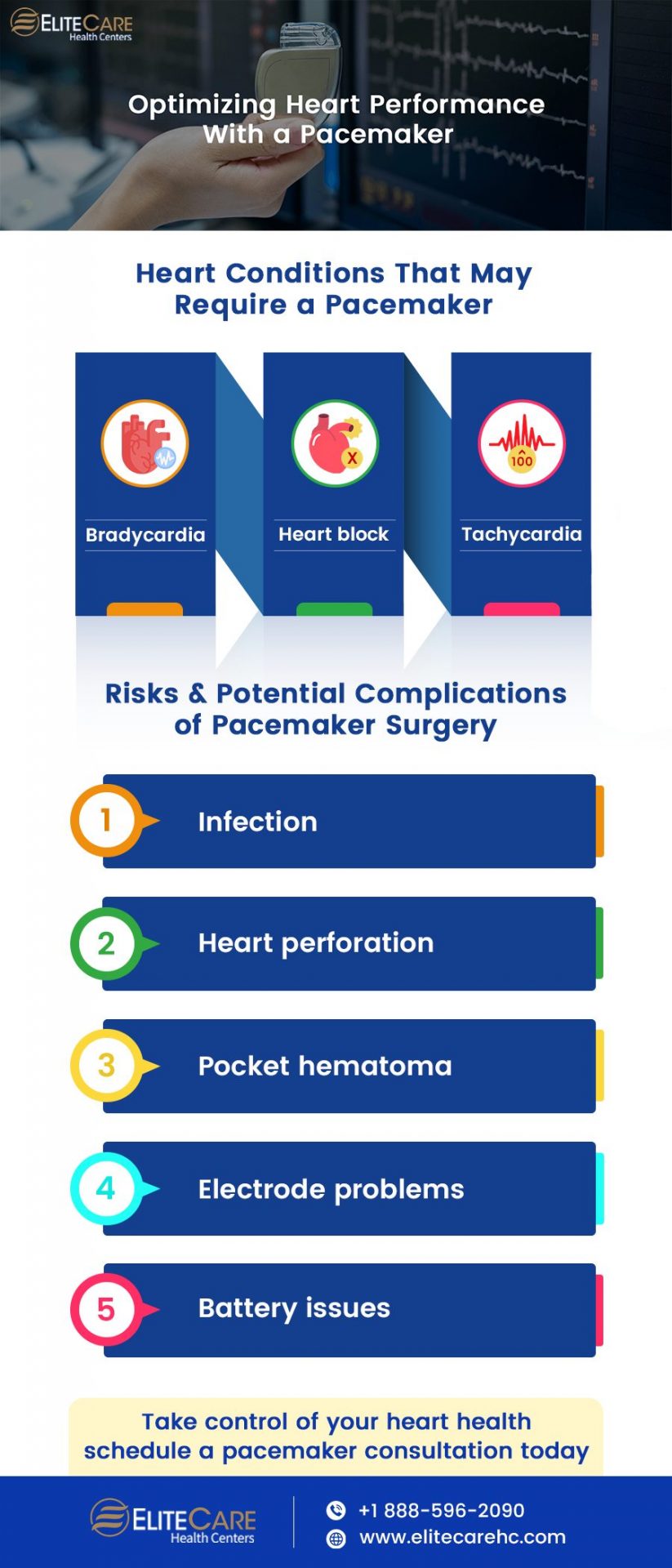
Heart disease is a severe health issue that affects millions of people around the world. It can manifest in various forms, including heart attack, heart failure, arrhythmias, and other conditions impacting the heart’s ability to function correctly. However, modern medical technology has provided a tool to help manage and treat heart disease: the pacemaker.
What is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered device implanted in the chest using a minor surgical procedure to help regulate heart rate and rhythm. The device contains electrodes connected to the heart and is used to detect the heart’s electrical impulses. When the heart rate falls below a certain level, or the rhythm becomes irregular, the pacemaker sends electrical signals to the heart to prompt it to beat at the correct rate.
The heart naturally regulates its beating rate. But some hearts don’t regularly beat due to a problem called arrhythmia. Often, a pacemaker device can be used to correct it.
Read More: Debunking 5 Common Myths about Heart Health in Women
How Does a Pacemaker Work?
The electrical impulses delivered by the pacemaker are designed to mimic the natural electrical signals produced by the primary pacemaker of the heart, the sinoatrial (SA) node.
Pacemakers can be programmed to deliver electrical impulses at specific intervals depending on the individual’s needs and heart condition. Additionally, some pacemakers are equipped with sensors that detect changes in the individual’s activity level or heart rate and can adjust its signals accordingly to optimize the heart’s performance.
The battery life of a pacemaker varies depending on the type of device and the frequency of use. Most pacemakers have a battery life of 5-15 years and can be replaced if necessary. The replacement is a minor procedure that is performed under local anesthesia.
Heart Conditions That May Require a Pacemaker
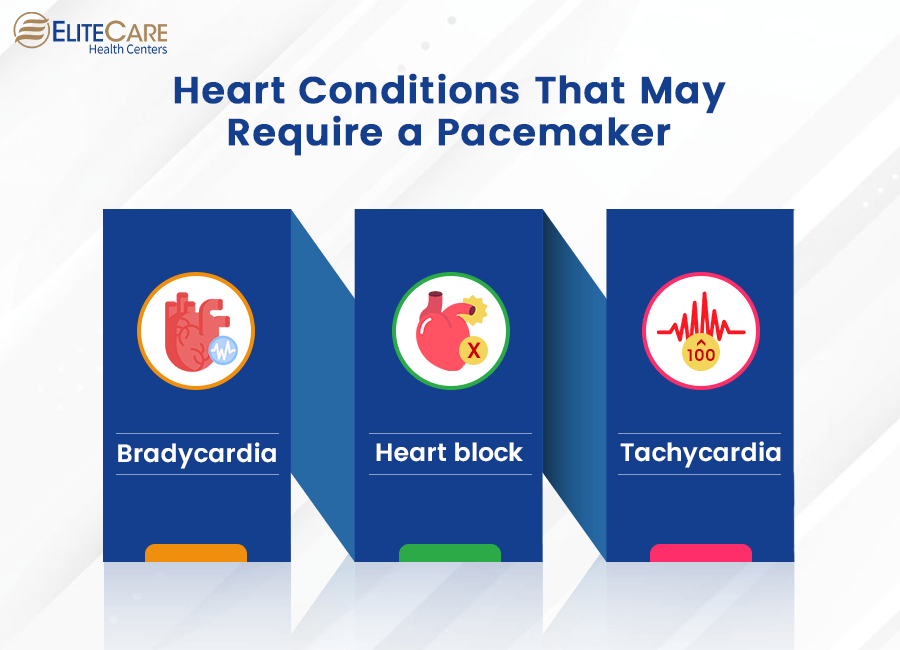
- Bradycardia is when the heart beats too slowly, usually at fewer than 60 beats per minute. This slow heart rate can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, and fainting. Sometimes, it can lead to more severe complications such as heart failure or cardiac arrest.
- Heart block occurs when the electrical signals from the heart’s primary pacemaker are delayed or blocked, causing the heart to beat too slowly or irregularly, which can be dangerous.
- Tachycardia is a condition where the heart beats too fast, usually at a rate of more than 100 beats per minute. This fast heart rate can cause shortness of breath, lightheadedness, chest pain, and fainting. In severe cases, tachycardia can lead to heart failure and other complications.
A physician prescribes a pacemaker after thoroughly evaluating the patient’s symptoms and medical history. Pacemakers are widely used and have a long history of success in helping people manage these conditions.
Read More: Best Ingredients to Make Heart Healthy Smoothies for Seniors
Types of Pacemakers
Several types of pacemakers are designed to treat specific heart conditions. The main types are:
- Single-chamber pacemaker: This type of pacemaker is used to treat bradycardia. The device has one electrode implanted in the heart’s right atrium and sends electrical impulses to regulate the heart rate.
- Dual-chamber pacemaker: This type of pacemaker has two electrodes, one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle and is used to treat more complex heart rhythm problems. It sends electrical impulses to both chambers of the heart, allowing it to beat in a coordinated manner.
- Biventricular pacemaker: This type of pacemaker is used to treat heart failure, a condition in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively. It has three electrodes, one in the right atrium and two in the right ventricle and sends electrical signals to coordinate the contraction of both ventricles.
The type of pacemaker best for an individual will depend on their heart condition, overall health, and other factors.
Read More: Everything You Need to Know About an EKG
Risks and Complications of Pacemaker Surgery
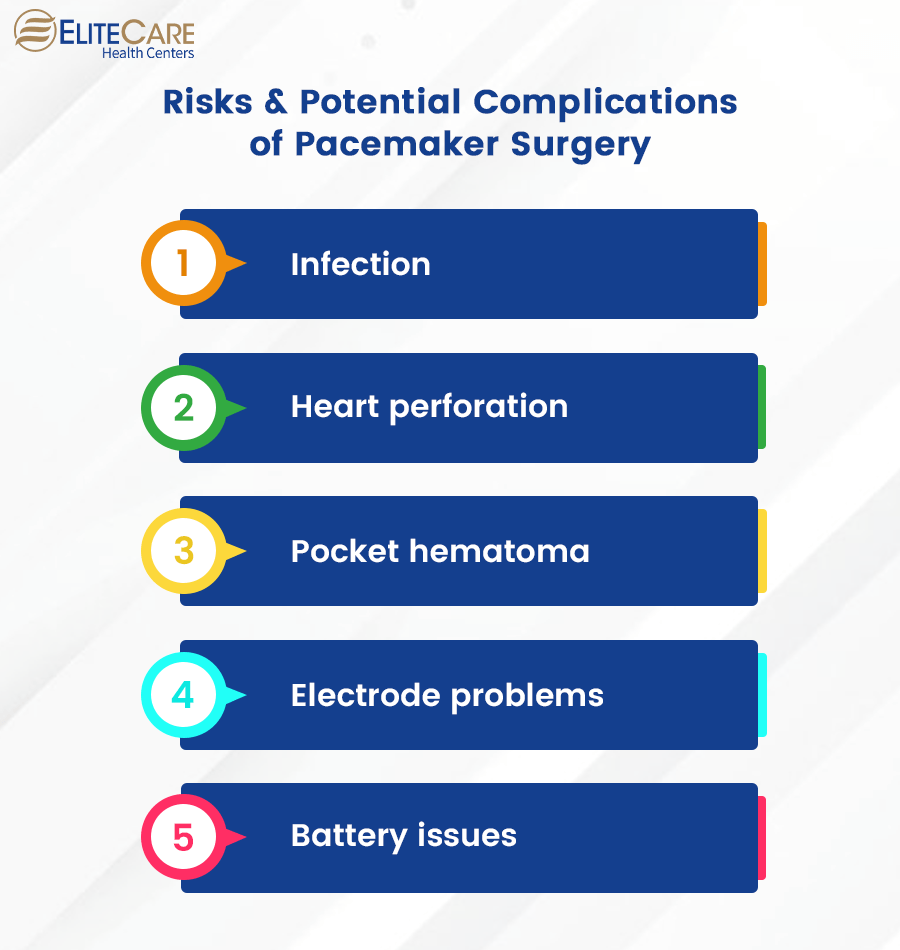
Pacemaker surgery is generally considered safe but comes with risks and potential complications, like any surgical procedure. Some common risks and side effects of pacemaker for seniors include:
- Infection: The incision site or where the device was implanted can become infected, leading to redness, swelling, and pain. The risk of infection can increase in older adults or individuals with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or other medical conditions. In some cases, the infection may require additional treatment.
- Heart perforation: In rare cases, the pacemaker leads can puncture the heart or blood vessels, causing internal bleeding. This can lead to bleeding or fluid buildup in the heart and cause serious complications.
- Pocket hematoma: It is a common complication, particularly in seniors. It occurs when there is bleeding around the pacemaker pocket, the small incision made in the chest to hold the pacemaker in place. This bleeding can lead to a buildup of blood around the device, causing pain and discomfort. In some cases, a hematoma can also pressure the pacemaker, potentially leading to device malfunctions or electrical problems.
- Electrode problems: In pacemaker electrode problems can occur after surgery and lead to issues with the device’s ability to regulate the heart rate. This can lead to arrhythmias, chest pain, shortness of breath, and even heart failure. Surgery may be required to correct the problem.
- Battery issues: This can occur for several reasons, including the age of the device, frequency of use, and the individual’s overall health. Over time, the battery in a pacemaker may lose its ability to hold a charge, leading to a decrease in the device’s performance and the need for replacement.
Seniors need to understand pacemaker surgery’s risks and potential complications, but it’s equally important to remember that the procedure is generally safe and effective in treating heart conditions. If a physician recommends a pacemaker, it’s because they believe it is the best option for improving heart function and quality of their patient’s life.
Read More: What to expect from an annual physical exam
Maintenance and Care of a Pacemaker
- Regular check-ups – Usually every 3 to 6 months, it is crucial to schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider to monitor the pacemaker’s performance and check for any issues that may arise.
- Battery replacement – The battery in a pacemaker has a limited lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced. Regular check-ups will help to determine when this is necessary.
- Avoiding activities that may interfere with the pacemaker – It is essential to follow some general guidelines. The person should avoid close proximity to strong electromagnetic fields, such as those produced by large appliances, heavy machinery, and high-voltage equipment. Strong magnets such as those in MRI machines can affect and even restrict the performance of pacemakers. Seniors should also avoid activities that involve strong movement or jolting of the chest area, as they may can cause damage to a pacemaker or its leads. Additionally, when passing through airport security, inform security personnel of your pacemaker. A handheld metal detector or full-body scanner may be used, both of which are safe for pacemaker patients.
Conclusion
The World Health Organization estimates cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death globally, accounting for over 17 million deaths yearly. Pacemakers have proven to be life-saving and crucial for optimizing heart performance. They are especially crucial for seniors with a higher likelihood of experiencing heart problems. If the senior is experiencing heart problems, it is imperative to speak with a physician at a medical clinic such as EliteCare Health Centers or for emergencies, call 9-1-1 or go to the nearest Emergency Room.